Currently, there is a tendency to move from single-component catalysts of simple composition to complex multi-component and multifunctional, such as complex-based catalysts. It was noted that the catalytic activity of the complex compound with the metal increases precisely with the chelate structure of the complex.
One of the known applications of copper complexes relates to their use as catalysts in various oxidation reactions, while cyclohexane oxidation is an important and widely studied catalytic conversion, which is carried out by industrial chemical processes, but with low conversions and low selectivity, therefore it is of great practical interest to develop more effective, as well as easily synthesized, reusable and environmentally friendly catalyst for this oxidation process.
The selective oxidation of alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes or ketones is another fundamental transformation in both laboratory and industrial syntheses, often used, for example, for the preparation of pharmaceuticals, flavors and fragrances. In this case, the development of new catalytic oxidation systems with high selectivity using cheap and environmentally friendly oxidizing agents (for example, molecular oxygen) is also very attractive.
The synthesis of new heteroligand water-soluble homogeneous copper (II) -based catalysts with N,O-containing ligands is promising for stereospecific C-H functionalization in an aqueous medium. Such catalysts can be successfully used in the synthesis of multifunctional compounds that are of interest in the molecular design of heterocyclic systems.
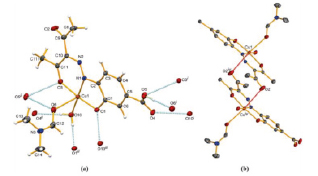
Pic. 1. ORTEP diagrams of complex 2 (a) with the atom numbering scheme and showing the interactions of hydrogen bonds, and (b) showing the bonding of neighboring molecules through intermolecular contact interactions of CuO, generating octahedral binuclear aggregates. Ellipsoids are drawn with probability
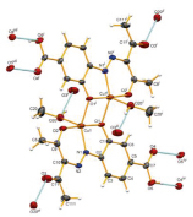
Pic. 2. Scheme ORTEP complex 3 with atomic numbering scheme and showing the interaction of hydrogen bonds. Ellipsoids are drawn with a 50 % probability
It was found that 3-(2-hydroxy-4-carboxyphenylhydrazone) pentane-2,4-dione has a good synthetic potential for complexation with copper (II), acting as a suitable ligand to create water-soluble complexes 2 and 3.
Complexes 2 and 3 act as catalyst precursors for acid-free peroxidative oxidation of cyclohexane to a mixture of cyclohexyl hydroperoxide (primary product), cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone (mass and yields up to 163 and 14.4 %, respectively), as well as for selective aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohols to benzaldehydes in aqueous solution under mild conditions (mass and yields up to 390 and 94 %, respectively). In alkane oxidations 2 and 3, apparently, behave as «dual role catalysts» that combine an active metal center and an acid promoter group in one molecule.

